Security and Data access are controlled by different set of tools like Profiles, Roles, Permission sets, Sharing Settings and Page Layouts etc
Why do we need a
Profile?
Profiles (mandatory
for User) determine which Objects and Fields
User can access. This will determine what access they have in the system
Why Permission Sets?
When you want to
provide additional access to some users with same profiles, Permission sets are
created and assigned to selected users.
Role : Grant Record
access using hierarchies
Why a Role when User
has a Profile ?
Roles determine your
position in hierarchy for Record visibility while Profile determine what User
can see
If you are above
someone in Role hierarchy, you can automatically see records of all users under
his hierarchy though permissions are PRIVATE
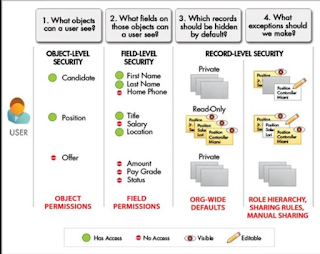
4 Levels of
Restrictions to what Users can see :
App Level : Hide the App from Users
Profile Permissions: Visible, Default(
To make it a default App when User login )
Object Level : Hide Tab from User
Profile Permissions: Read, Create,
Edit, Delete
Field Level :
Hide Field from User
Profile
Permissions(Setup > Profiles > Object > Field ) à Read
and Edit
(or)
Field
level Security for Profiles (Setup> Object > Field > Field Level
security) à ReadOnly and Visible(Read+Write)
Updating
at Profile level can only restrict for that profile. If there are more than one
profile to restrict, go with Field level Security to update access for multiple
profiles.
Record Level : Hide Records from Users
Note: Records cannot be restricted at Profile level
Achieved by :
Gate 1: OWD ( Org
wide default settings) , Gate 2: Role Hierarchy , Gate 3: Sharing Rules , Gate
4 : Manual Sharing by record owner
To specify
record-level security, set your organization-wide sharing settings, define
Roles, and create sharing rules
Organization-wide sharing settings specify the
default level of access users have to each other's records (Gate 1 for record
access)
Role Hierarchy : Once you've specified
organization-wide sharing settings, the first way you can give wider access to
records is with a role hierarchy.
Sharing rules let you make automatic exceptions to
organization-wide sharing settings for particular sets of users, to give them
access to records they don't own or can't normally see.
Manual Sharing : record owners can use manual
sharing to give read and edit permissions to users who would not have access to
the record any other way.
Note : Sharing rules and role
hierarchies, are only used to give additional users access to records—they
can't be stricter than your organization-wide default settings.
sad
ReplyDeleteadana
ReplyDeleteadıyaman
afyon
ağrı
aksaray
50V
bitlis
ReplyDeletetunceli
ardahan
bingöl
muş
WJZ
van
ReplyDeletekastamonu
elazığ
tokat
sakarya
3BSİQE
B387B
ReplyDeleteTekirdağ Parke Ustası
Siirt Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Giresun Parça Eşya Taşıma
Muğla Lojistik
Yalova Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Manisa Parça Eşya Taşıma
AAX Güvenilir mi
Kırıkkale Evden Eve Nakliyat
Van Lojistik
16096
ReplyDeleteÇerkezköy Çatı Ustası
Pi Network Coin Hangi Borsada
Bitget Güvenilir mi
Poloniex Güvenilir mi
Kilis Evden Eve Nakliyat
Balıkesir Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Big Wolf Coin Hangi Borsada
Gölbaşı Parke Ustası
İstanbul Şehirler Arası Nakliyat
43453
ReplyDeletebybit
canlı sohbet ucretsiz
mexc
en güvenilir kripto borsası
kucoin
telegram kripto para
kraken
huobi
canlı sohbet siteleri
11700
ReplyDeletebtcturk
bitcoin ne zaman çıktı
okex
https://kapinagelsin.com.tr/
telegram kripto para kanalları
binance referans kimliği nedir
aax
4g mobil proxy
btcturk
D11B6
ReplyDeletereferans kimliği nedir
April 2024 Calendar
August 2024 Calendar
filtre kağıdı
referans kodu
bingx
January 2024 Calendar
kucoin
kripto kanalları telegram
D905154370
ReplyDeletewhatsapp görüntülü show güvenilir
fx15 zayıflama hapı
lifta
telegram show
sinegra 100 mg
cam şov
cam show
geciktirici jel
ücretli show
2B354B65CD
ReplyDeletebeğeni satın alma
1B0820A8F1
ReplyDeletetwitter beğeni
308D2D96D2
ReplyDeletemmorpg oyunlar
sms onay go
mobil ödeme bozdurma
tiktok takipci satin alma
-